Top 10 Rainforests with Endangered Species
Rainforests are vital ecosystems that harbor an incredible diversity of life, including numerous endangered species. The top ten rainforests, such as the Amazon, Congo, and Southeast Asian rainforests, play a critical role in global biodiversity, climate regulation, and indigenous cultures. Unfortunately, these rich habitats face significant threats from deforestation, climate change, and human encroachment, putting countless species at risk of extinction.
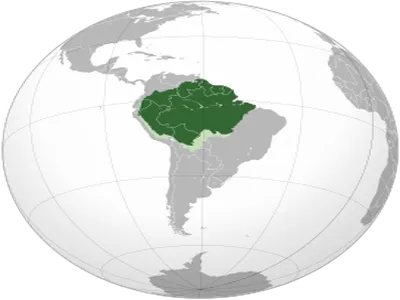
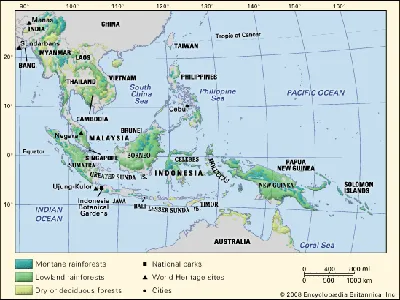
The Amazon Rainforest, often referred to as the "lungs of the planet," is home to a vast array of endangered species, including the jaguar, the Amazon river dolphin, and the critically endangered Spix's macaw. The Congo Basin, the second-largest rainforest, supports unique wildlife such as the forest elephant and the bonobo, both facing severe habitat loss. Southeast Asia's rainforests are equally rich, hosting endangered species like the Bornean orangutan and the Sumatran tiger. These rainforests are not just crucial for wildlife; they also provide essential resources for local communities and serve as significant carbon sinks. Protecting these ecosystems is not only imperative for the survival of their endemic species but also for maintaining the ecological balance and combating climate change. Efforts to conserve these rainforests include establishing protected areas, promoting sustainable land use practices, and raising awareness about the importance of preserving biodiversity.

 View All
View AllAmazon Rainforest - Biodiverse ecosystem; home to many endangered species.

 View All
View AllCongo Rainforest - Biodiverse, vital ecosystem; home to endangered species like gorillas.

 View All
View AllMadagascar Rainforest - Biodiverse habitat, unique species, conservation critical, endangered wildlife.

 View All
View AllSoutheast Asian Rainforest - Biodiverse habitat, home to endangered species like orangutans.

 View All
View AllDaintree Rainforest - Ancient rainforest, rich biodiversity, home to endangered species.

 View All
View AllAtlantic Forest - Biodiverse ecosystem, home to many endangered species.

 View All
View AllCloud Forests of Central America - Misty, biodiverse ecosystems harboring unique endangered species.

 View All
View AllPacific Northwest Rainforest - Lush ecosystem, diverse species, threatened habitats, conservation needed.

 View All
View AllSundarbans Mangrove Forest - Biodiverse mangrove habitat, home to endangered Bengal tigers.

 View All
View AllPhilippine Rainforest - Biodiverse ecosystem, home to endangered species, critical conservation area.
Top 10 Rainforests with Endangered Species
1.
Amazon Rainforest
Pros
Biodiversity hotspot
vital carbon sink
Indigenous cultures thrive
medicinal resources abound
essential global climate regulator.
Cons
Deforestation threatens biodiversity
illegal logging disrupts ecosystems
climate change impacts rainfall patterns
habitat fragmentation endangers species
pollution affects water quality.
2.
Congo Rainforest
Pros
Biodiversity hotspot
vital carbon sink
indigenous cultures thrive
unique ecosystems
crucial for global climate regulation.
Cons
Deforestation threatens biodiversity
poaching endangers wildlife
climate change impacts ecosystems
mining damages habitats
human conflict disrupts conservation efforts.
3.
Madagascar Rainforest
Pros
Biodiversity hotspot
unique flora and fauna
vital for global climate regulation
rich cultural heritage
opportunities for ecotourism.
Cons
Deforestation threatens biodiversity
invasive species disrupt ecosystems
climate change impacts habitats
limited conservation funding
human-wildlife conflict increases.
4.
Southeast Asian Rainforest
Pros
Biodiversity hotspot
vital carbon storage
supports indigenous cultures
essential for global climate regulation
unique medicinal resources.
Cons
Deforestation threatens biodiversity
habitat destruction increases
illegal logging persists
climate change impacts ecosystems
poaching endangers wildlife.
5.
Daintree Rainforest
Pros
Biodiversity hotspot
unique ecosystems
ancient plant species
habitat for endangered wildlife
cultural significance to Indigenous peoples.
Cons
Limited accessibility
high humidity and heat
potential for dangerous wildlife encounters
invasive species threats
impact of climate change.
6.
Atlantic Forest
Pros
High biodiversity
unique ecosystems
critical for climate regulation
rich cultural heritage
home to many endemic species.
Cons
Deforestation threatens biodiversity
habitat fragmentation disrupts ecosystems
invasive species outcompete natives
climate change impacts resilience
illegal logging endangers species.
7.
Cloud Forests of Central America
Pros
Biodiversity hotspot
unique ecosystems
crucial water source
climate regulation
habitat for endangered species.
Cons
Habitat loss due to deforestation
climate change impacts on biodiversity
limited access for conservation efforts
invasive species threats
and human-wildlife conflict.
8.
Pacific Northwest Rainforest
Pros
Biodiversity hotspot
unique ecosystems
carbon sequestration
cultural significance
stunning landscapes.
Cons
Limited sunlight affects plant growth
heavy rainfall causes erosion
invasive species threaten native wildlife
logging impacts habitat
climate change disrupts ecosystems.
9.
Sundarbans Mangrove Forest
Pros
Biodiverse habitat for endangered species
protects coastal areas from erosion
supports local livelihoods through fishing
essential for carbon sequestration
attracts eco-tourism.
Cons
Deforestation threats
Climate change impact
Poaching of wildlife
Pollution from industries
Human-wildlife conflict.
10.
Philippine Rainforest
Pros
Biodiversity hotspot
unique ecosystems
indigenous cultures
carbon storage
medicinal resources.
Cons
Deforestation threatens biodiversity
illegal logging damages ecosystems
mining disrupts habitats
climate change impacts species survival
poaching endangers wildlife.
Similar Topic You Might Be Interested In
- Top 10 Ancient Ruins Hidden in the Jungle
- Top 10 Archaeological Sites Rediscovered in the Last Century
- Top 10 Roman Amphitheaters Outside Italy
- Top 10 Stone Circles Older Than Stonehenge
- Top 10 Historic Villages Preserved in Time
- Top 10 Viking Sites and Relics in Europe
- Top 10 Medieval Castles Built on Cliffs
- Top 10 Fortified Cities from Ancient Civilizations
- Top 10 Famous Battlefields to Visit
- Top 10 Best-Preserved Medieval Walled Towns